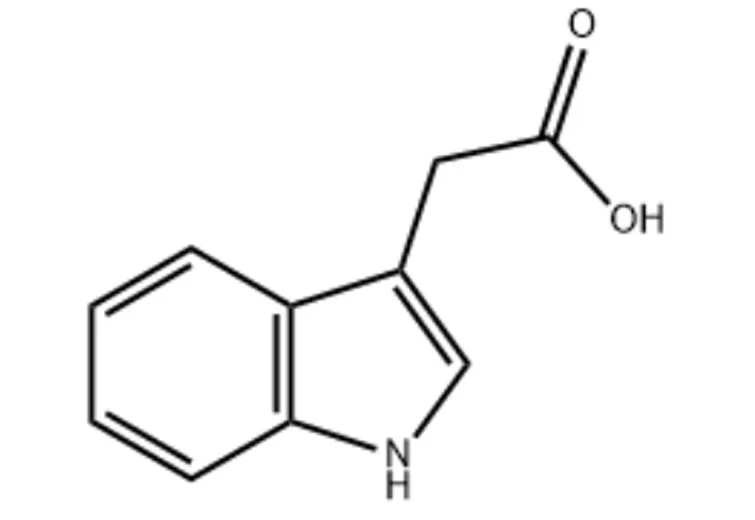
3-Indoleacetic acid
1. Appearance:Off White crystalline powder
2. Usage: 3-Indoleacetic acid is a plant growth regulator, it can promote cell division, accelerate root formation, increase fruit setting and prevent fruit drop
3.Customerized packing label
4.Professional registration GLP,ICAMA,LOA etc.
5.FAO standard
What Our Customers Say About 3-Indoleacetic Acid (IAA)
3-Indoleacetic Acid (IAA) FAQs
-
80%High PurityEnsure the reliability of each product.
-
58%Fast-Acting FormulaQuickly provide visible effects
-
What are the natural roles of IAA in plant physiology?
What are the natural roles of IAA in plant physiology?
As the primary endogenous auxin, IAA regulates phototropism, gravitropism, apical dominance, and vascular differentiation. In agriculture, synthetic IAA applications mimic these natural processes to stimulate adventitious root formation, enhance graft union success, and improve stress recovery in transplanted seedlings.
-
How is IAA typically applied in horticultural practices?
How is IAA typically applied in horticultural practices?
Common methods include rooting hormone dips (500-1500 ppm for cuttings), foliar sprays (10-100 ppm for stress mitigation), and tissue culture media supplementation (0.1-5 mg/L). Seed treatments (1-10 ppm) improve germination uniformity in hard-to-sprout species.
-
What plant propagation benefits does IAA provide?
What plant propagation benefits does IAA provide?
It increases rooting percentages (by 30-70% depending on species), accelerates root initiation timing (by 5-10 days), and enhances root system architecture with more fibrous secondary roots compared to untreated controls - critical for successful transplant establishment.
-
How does IAA concentration affect plant responses?
How does IAA concentration affect plant responses?
Responses follow a strict dose curve: low concentrations (0.1-1 ppm) stimulate root initiation, moderate levels (1-10 ppm) promote cell elongation, while high doses (>50 ppm) inhibit growth and may induce ethylene-related stress responses. Optimal rates vary dramatically between species and even cultivars.
-
How does IAA interact with other phytohormones?
How does IAA interact with other phytohormones?
It exhibits complex crosstalk - synergistic with cytokinins for callus induction but antagonistic for shoot/root determination. Balanced ratios with abscisic acid regulate stress responses, while ethylene biosynthesis often follows IAA application peaks.